Many scientific disciplines employ Agilent UV VIS spectroscopy, from bacterial culture, drug identification, and nucleic acid purity checks and quantification. It is also used for quality control in the beverage industry and chemical research for various applications. But, how does UV VIS spectroscopy works, and how can it help your research? Read on and know the answers to these questions.
Understanding UV-VIS Spectroscopy
Table of Contents
Substances may be classified and studied using UV/VIS light, frequently used in research, manufacturing, and quality control. Generally, spectroscopy in the UV/VIS range relies on the sample’s ability to absorb light.
It is possible to determine a sample’s purity by measuring the quantity of light absorbed and the wavelength. Quantitative analysis using optical spectroscopy is feasible because the amount of light absorbed is proportional to the sample volume.
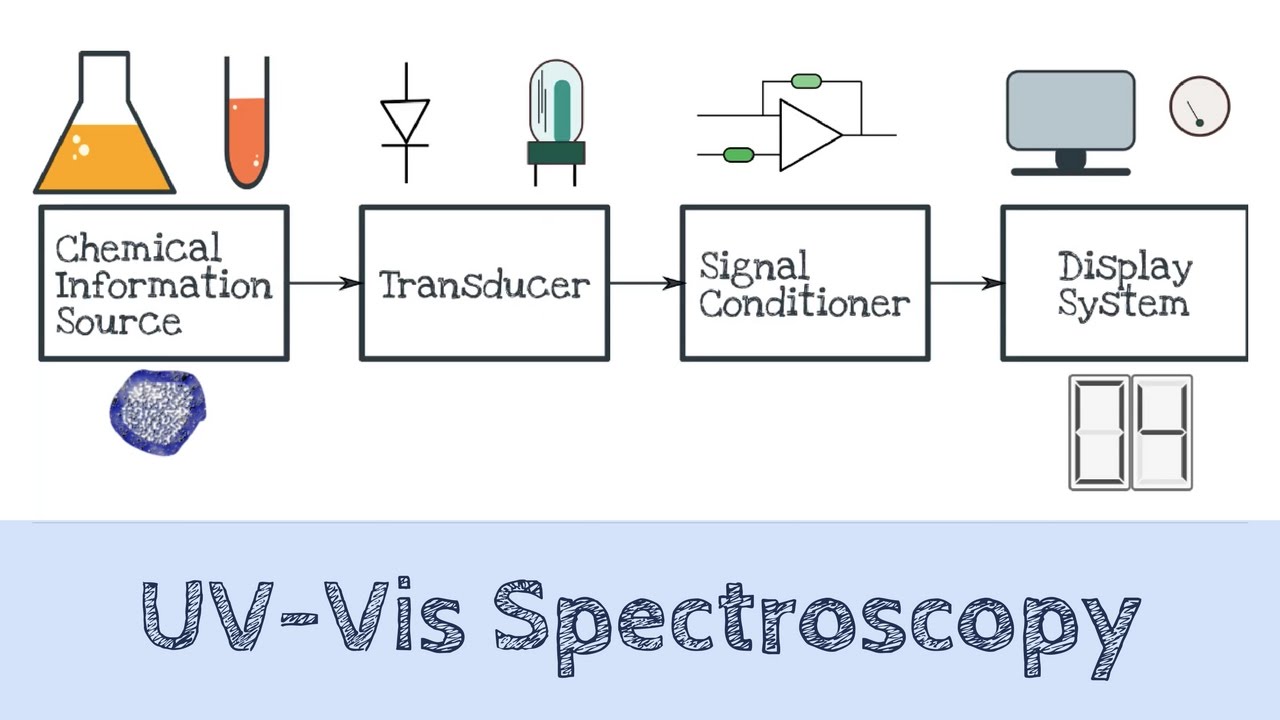
How UV-VIS Spectroscopy Works
The intensity of light passing through a sample solution in a cuvette is measured by a UV/VIS spectrophotometer and compared to the power of light preceding the sample. In fact, a light source, sample container, dispersive device, and detector are the most significant parts of the UV/VIS spectrum spectrophotometer.
This device measures transmittance, the ratio of the transmitted light intensity I to the starting light power. In addition, the instrument reports the Absorbance, defined as A = log a = 0 (Transmittance).
Applications of UV-VIS Spectroscopy
Quantitative and qualitative analysis are two main applications of UV-VIS spectroscopy. It may facilitate your study in the following ways.
Quantitative Analysis
Spectrophotometry, which measures how much light a material absorbs, uses UV-VIS spectroscopy. Light passing through a sample is measured when it passes through a reference sample or blank. Besides the above, it may also be used as follows:
Concentration
- Medicinal use of metal ions such as iron, copper, and nickel
- Water treatment involves the use of inorganic ions such as nitrate
- COD in Food and Beverage and Electroplating
Analyte Concentration Vs. Time
- A glucose oxidase enzyme converts -D-glucose to glucose (725 and 415 nm)
- Catalysis rate assessment utilizing enzyme kinetics in pharma
- Catalysis with Cholesterol Oxidase enhances cholesterol oxidation (500 nm)
- GPO colorimetric kinetic test (520 nm)
- Pyridine nucleotide phosphorylation/dehydration (NAD+/NADH)
Physical and Chemical World
- Consistently complex formations
- Dissolvability test
- pH as a function of acid dissociation time
- The coefficient of partitioning
Qualitative Analysis
In addition to quantitative analysis, examining the entire UV/VIS absorption spectra allows for identifying substances. Generally, the exact location and, to some degree, the absorption peaks profile allow for identifying individual chemicals.
Each sample has a distinct UV/VIS spectrum that may be utilized for identification. To do so, the spectrum of the sample is compared to known, pure compound spectra.
Conclusion
A UV-VIS spectrometer’s precision is the most crucial benefit for scientists using the gadget. Additionally, miniature UV-VIS spectrometers can provide incredibly exact readings, which is essential whether you are making chemical solutions or tracking the passage of celestial bodies. As a result, owning one will ease and quicken your study.